Metamorphism is a
process that causes changes in texture, mineralogy or both occurring in the
underlying rocks by diagenesis and weathering limit and upper limit is the
melting (fusion). The
process of change in texture that is not accompanied by changes mineraloginya
there are 2 kinds, namely: Cataclastic and recrystallization. Cataclastic
is the process of destruction on the rocks, while recrystallization is the
process of rearrangement of the crystal lattice and relationships in the grain
through the migration of ions and lattice deformation, without the destruction
of the granules. Neocristalisasi
is the process of forming new minerals that are not on the previous metamorphic
rocks. A similar
process occurs also during the process of diagenesis. So
metamorphism same may be said with diagenesis, but only includes the processes
that occur in the earth's surface (low p and t).
Metamorphic rocks
are rocks with textures and minerals that illustrates cataclastik,
recrystallization or neokristalisasi in response to different conditions of
formation of these rocks and processes between diagenesis and anatexis. Batua
common origin of these metamorphic from igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic
rocks themselves but to a lesser degree. Metamofisme,
may also occur at temperatures and pressures higher than 200oC and 300 MPa. Rocks
are exposed to the process of metamorphism may be located at a depth far from
the earth's surface as it occurs in a subduction zone or collision. The
upper limit of metamorphism occurs in pressure and temperature phase where the
rocks did not experience melting or smelting. If
you have experienced melting then it can no longer referred to as metamorphism.
Factors Affecting the metamorphism
Factors Affecting the metamorphism
Metamorphism
occurred because some minerals stable only under certain conditions of pressure
and temperature. When
there is change in pressure and temperature, chemical reaction occurs that
causes the minerals in rocks changed to achieve stability at a certain pressure
and temperature.
The Factors
Affecting metamorphism:
·
Geothermal Temperature Gradients along. Temperature
can also increase associated with igneous intrusions.
·
Pressure increases with increasing, then, both pressure
and temperature will vary in each depth. Pressure
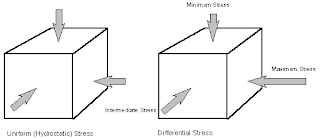
is defined as the force generated from all directions. There
are several types of stress, called hydrostatic stress, or uniform stress. If
stress is not the same from all directions, the stress is called differential
stress.
o
If there are current or differential stress during
metamorphism, will affect the texture of the rocks are formed.
o
Rounded grains can be aligned in the direction of maximum
stress.
minerals that crystallize or grow in the field of differential stress can have a better orientation. In particular, the silicate minerals (micas : Muscovite and biotite, chlorite, talc, and serpentine).
minerals that crystallize or grow in the field of differential stress can have a better orientation. In particular, the silicate minerals (micas : Muscovite and biotite, chlorite, talc, and serpentine).
Silica-Gazette
Gazette will grow with the sheets oriented perpendicular to the direction of
maximum sharpness (maximum stress). The
orientation of the sheets of silica can cause rupture of rocks along the
parallel sheet. Such
a structure is called foliasi.
·
Fluid Phase - Any space between the grains of minerals in
rocks potentially containing fluid. Most
of the fluid H2O, but can also contain dissolved minerals. Fluid
phase is important because the chemical reaction involving one turn into solid
minerals other solid minerals can be accelerated by the destruction of ions are
transported by the fluid itself. Along
with the increasing pressure of metamorphism, pore spaces in which the liquid
will be reduced.
·
Time - Chemical reactions in metamorphism, during
recrystallization, and formation of new minerals is running very slow. Through
laboratory experiments it is said that the process of metamorphism with a
longer time, will produce large grained minerals. Thus
the coarse grained metamorphic rocks have been through a long phase of
metamorphism. Experiments
stating that the time involved is millions of years.
This type of metamorphism
1) Based on the area
and volume
·
local metamorphism is metamorphism in rocks of relatively
small volume (less than 100 km ²)
·
regional metamorphism is metamorphism that occurs in a
relatively large volume of rock (thousands of cubic kilometers)
2) Based on the agent
metamorfismenya
·
contact metamorphism, metamorphism with the main agent is
the temperature that occurs due to igneous intrusions on the cooler shallow
rocks are common on local scales. This contact is called contact
aurele.
·
dynamic metamorphism is metamorphism that occurs due to
deviatoric stress. This
type occurs in fault zones and areas affected by meteoric jadtuah. This type
occurs in a fairly wide area.
·
static metamorphism is metamorphism that occurs due to
lithostatik which occurred at a depth of the relatively deep, as in the fore
arc basin and trough.
·
dinamotermal metamorphism, metamorphism merupakam the
most common and occur akabat combination of pressure and temperature.
Classification of metamorphic rocks (Based on its
chemical composition)
This classification
is in the review of the chemical elements contained in the metamorphic rock
that would characterize his native rock. Based
on the chemical composition of metamorphic rocks are divided into 5 groups,
namely:
·
Calcic metamorphic rock is a metamorphic rock derived
from rocks that are Classical (Al-rich element), generally composed of mudstone
and shale. Example:
batusabak and Phyllite.
·
Quartz Feldsphatic Rock is a metamorphic rock derived
from rocks rich in quartz and feldspar elements. Example: Gneiss
·
Calcareous metamorphic Rocka dalah metamorphic rocks
derived from limestone and dolomite. Example:
Marble
·
Basic metamorphic rock is a metamorphic rock derived from
alkaline igneous rocks, semibasa and medium enterprises, as well as tuffs and
sedimentary rocks that are napalan with the content of the element K, Al, Fe,
Mg.
·
Magnesia is a metamorphic rock metamorphic rock derived
from Mg-rich rocks. Example:
serpentit, schists.
Structure and texture of metamorphic rocks
The structure is a
form of handspecimen or the larger rocks. Structure
based on its scale textures dibedakand ari Diman is a form of microscopic
textures sidudun by size, shape, orientation, and egg relationship. In
metamorphic rocks occur because the process of deformation structures.
Textures in
metamorphic rocks:
1.
texture foliasi, namely the parallel orientation of the
minerals that show the bedding and the appearance of straightness. Examples of this texture, namely:
·
slaty texture, very fine grains (<0.1 mm),
straightness on the orientation planardan subplanar, fractions are pages. Examples of rock is slate.
·
Texture phylitic, very fine grained to fine (<0.5 mm),
the rock sample is phylite.
·
Texture schistose, fine-grained to very coarse (> 1
mm), examples of rock is schist.
·
gneissose texture, fine to very coarse grained, showing
bedding because of differences in mineralogy.
·
Texture foliasi porphyroblastik, very fine grained to
very coarse with a large crystal size (porphyroblastik) embedded in a matrix of
fine-sized berfoliasi
·
mylonite texture.
2.
Texture diablastik, texture characterized by the absence
of alignment buturan, oriented radially to the random texture example of this
is:
·
Texture sheaf, which shows the texture of the grains
which berdabang.
·
Texture spherolublastik, namely granular texture which
shows the radial group.
·
Texture fibroblastic, texture diablastik of similar size
3.
Texture Grano blastik
·
Texture homogranular, is showing the texture of the grain
size is nearly equal.
·
Texture heterogranular, a texture that shows non-uniform
grain size.
·
Texture heterogranoblastik, a texture which is
characterized by the same mineral kumpulam taapi with diverse sizes.
·
Texture nodularblastik texture, a texture that has
nodular composed of small mineral with one or two minerals in the matrix that
has a different composition.









Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar